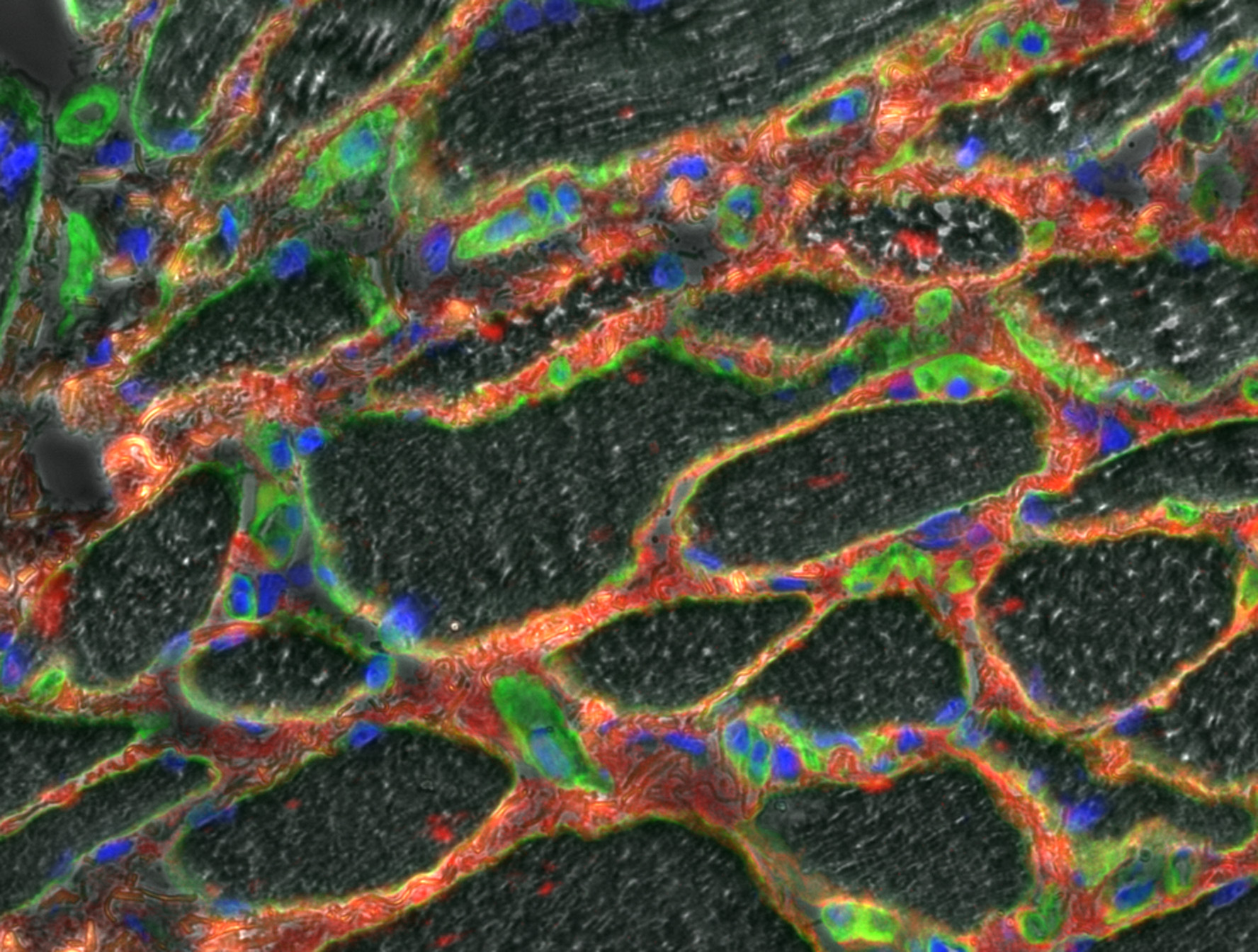
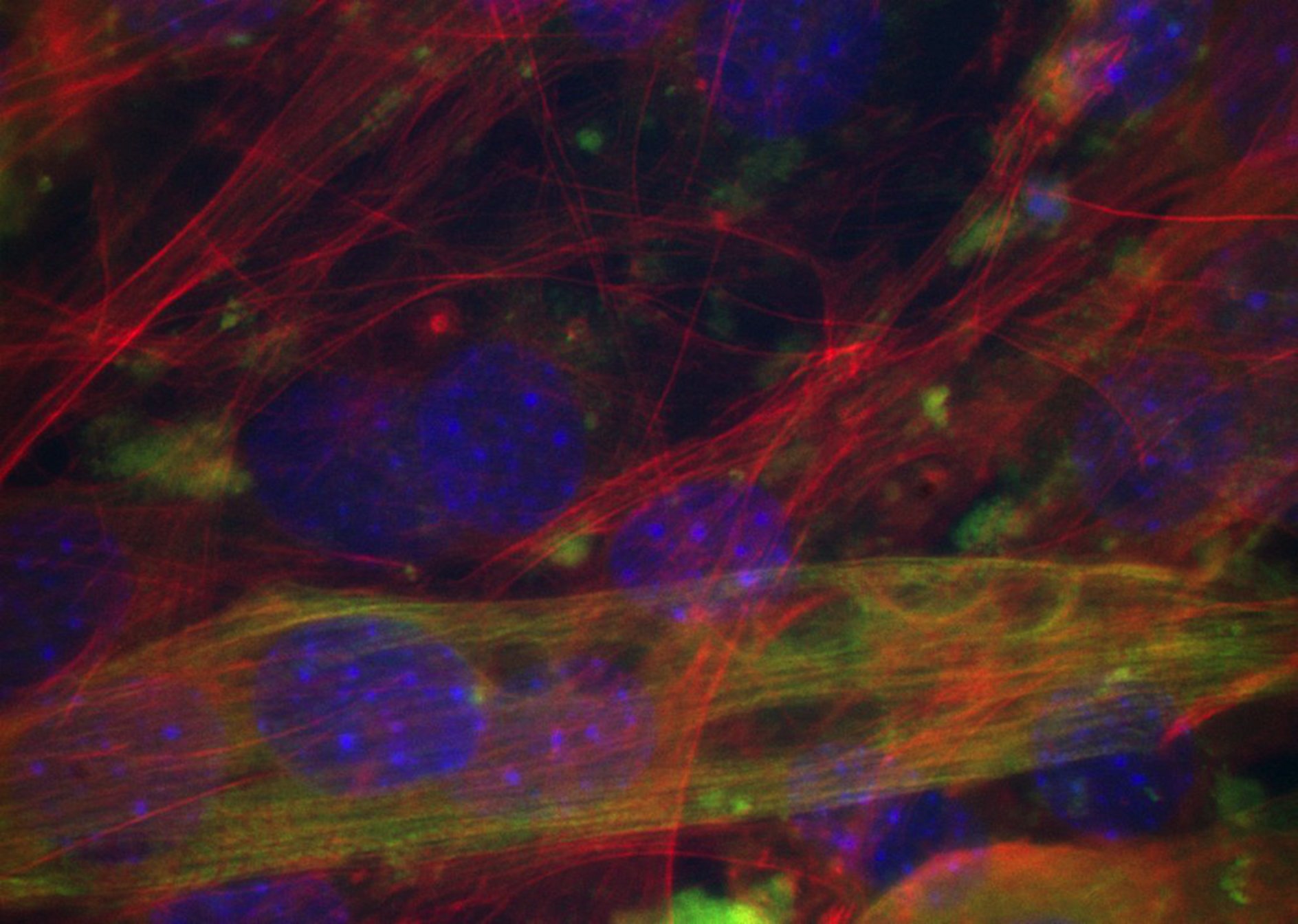
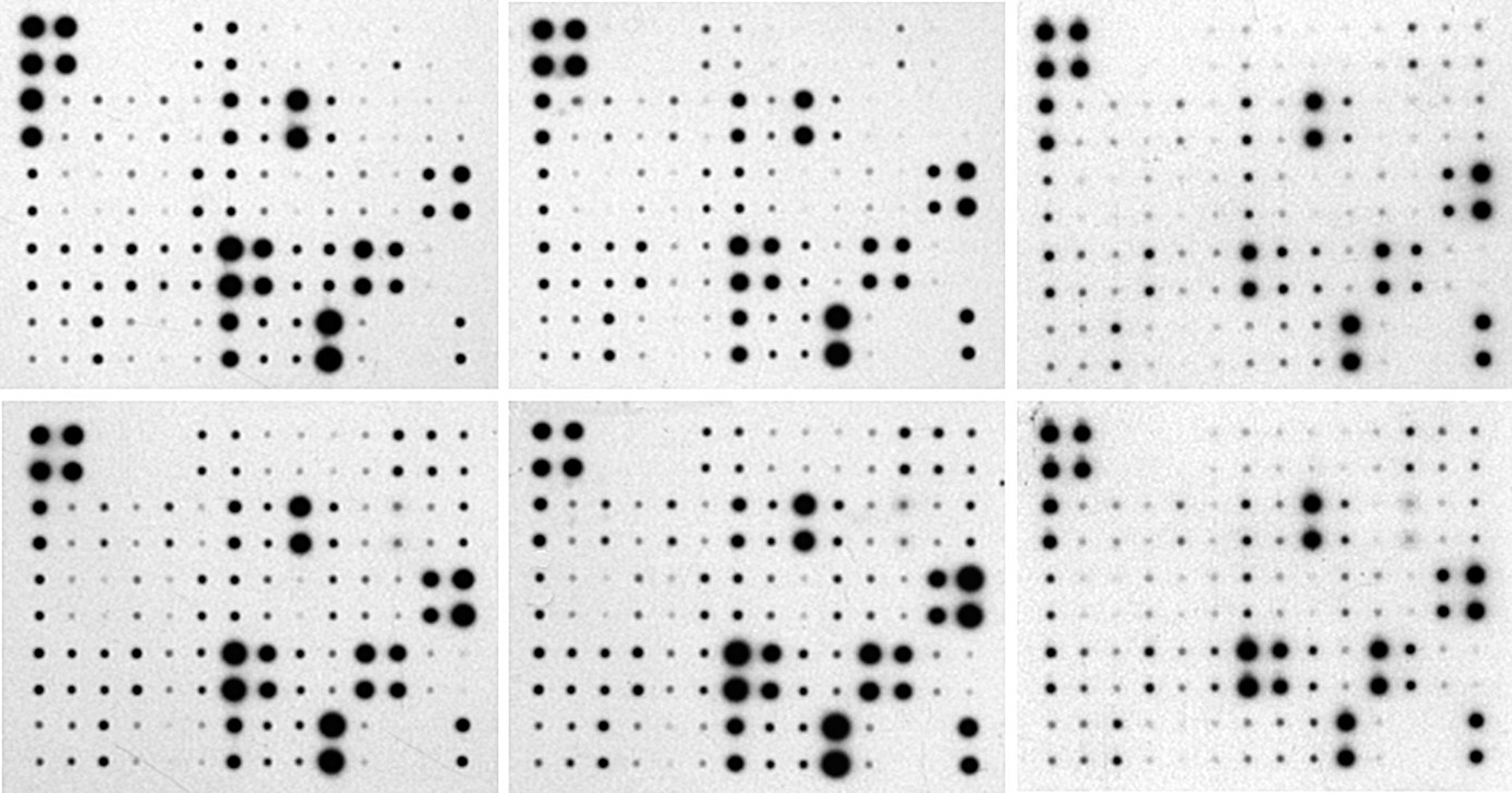
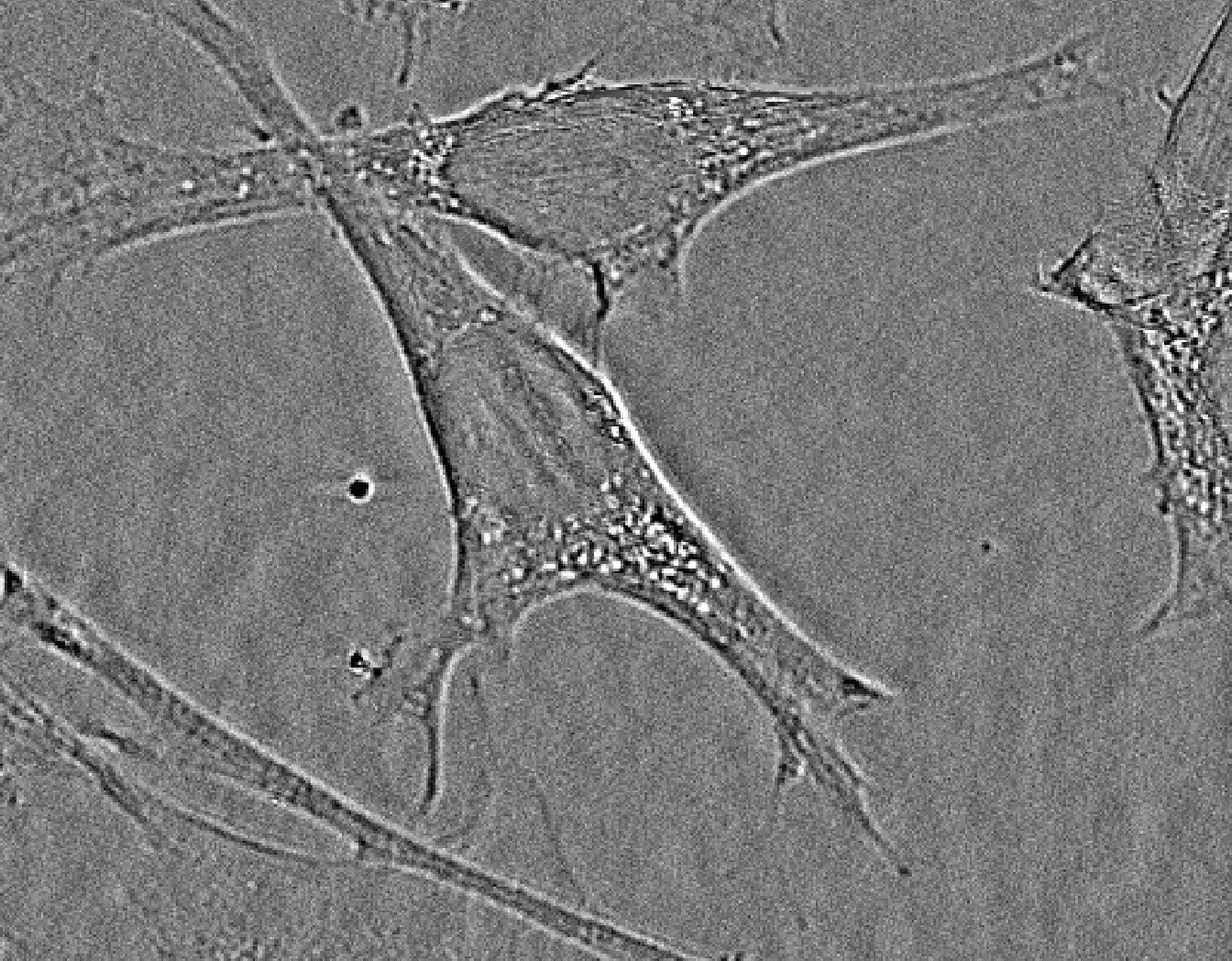
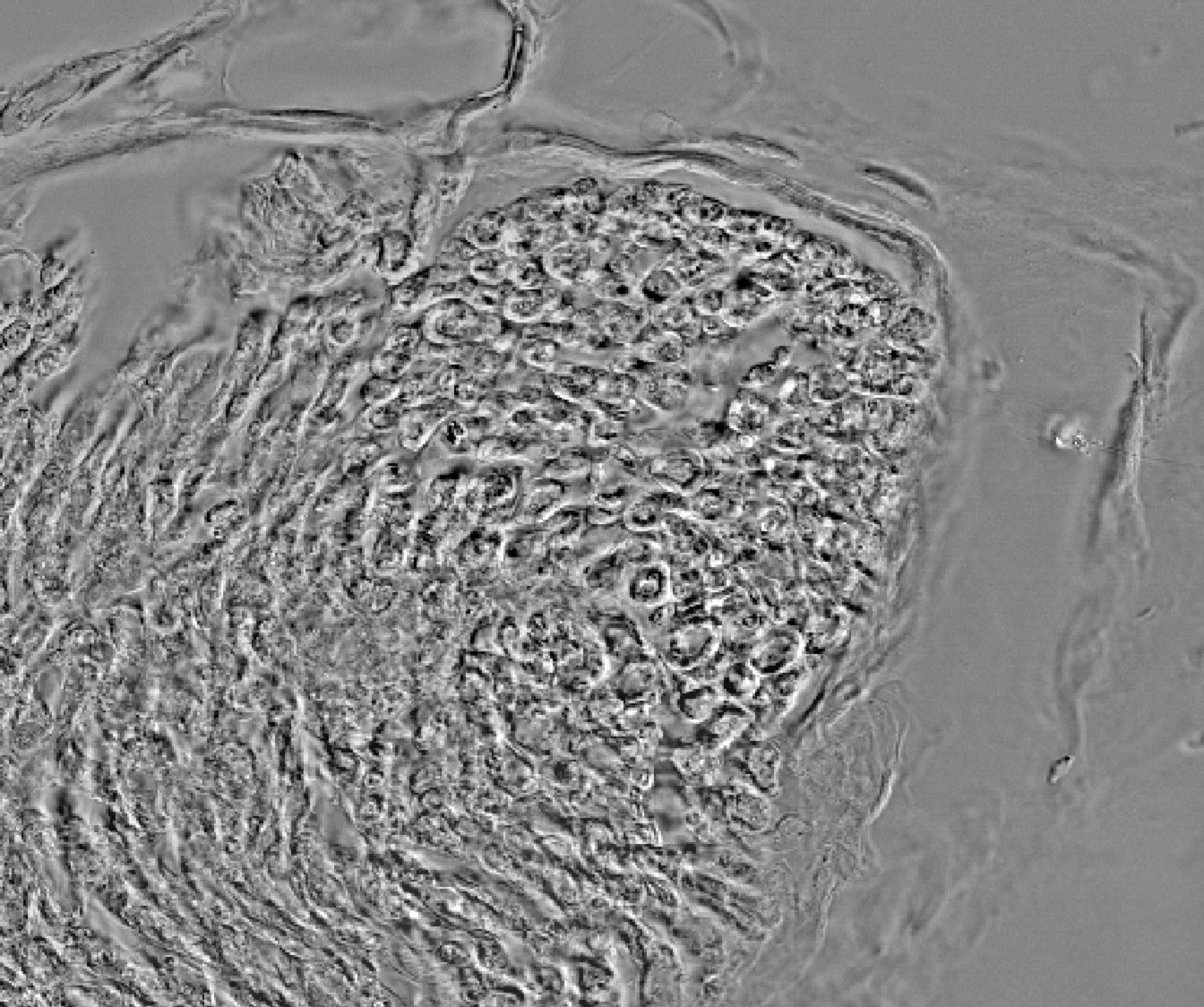
- Description, p1
- Installation, p2
- Documentation, p3
- Tutorial, p4
- Tutorial - build a composite, p4
- Tutorial - adjust levels (...), p4
- Tutorial - adjust levels (...), p4
- Tutorial - Range image (...), p4
- Video Tutorials, p5
- References, p6
Documentation:
-
"Stacks Menu Tool":


- "Multi-Channels Stack From Single Channel Files" Makes composite images from single channel images.

- "Stack to Hyperstack" Allows to open stacks as hyperstacks (multidimensional stacks)
- =>The "Stack to Hyperstack..." and the "Channels Tool..." functions of ImageJ are available by right-click menu. See the 28.7.1 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.

- "Multi-Channels Stack From Single Channel Files" Makes composite images from single channel images.
-
"Make Composite Tool" :
Converts stacks and hyperstacks into composite (multi channels) images and hyperstacks, allowing the choice of the color affected to each channel.

 The "Channels Tool…" of ImageJ is available by right-click menu. See the 28.7.5 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.
The "Channels Tool…" of ImageJ is available by right-click menu. See the 28.7.5 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.

-
"Adjust Channel Levels Menu Tool" :
allows several automatic level adjustments according to different bit depths.

- "8 bit sampling (0-255)" .../... "16 bit sampling (0-65535)" functions allow level adjustments according to different bit depths (8, 10, 12, 15 and 16).
- "min->max all channels" Permits an optimization of the channel LUTs between the minimum and the maximum of all channels.
- "min->max each channel" Permits an optimization of the channel LUTs between the minimum and the maximum of each channel. Several options are available for this function, see the tutorial for more details.

- "between two set values" Stretch the LUT between two manually set values.
- The "RGB Option" generates RGB documents after adjustments when activated. It is accessible for single action from the right-click menu.

-
"Adjust Min and Max Tool" :
Opens the "Color Balance" setting ImageJ window. See the 28.2.3 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.

-
"Z Projection Tool"
Provides a Z projection according to the maximum intensity of a stack.

 The full z projection options of ImageJ are available from the "Z Project…" right-click menu. See the 28.6.11 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.
The full z projection options of ImageJ are available from the "Z Project…" right-click menu. See the 28.6.11 sub-section in ImageJ User Guide for details.

-
"Remove Current Channel Tool" :
Remove the active channel.

 The full options of ImageJ to remove slices are available from the "Delete Slice" click right menu. See the ImageJ User Guide for details.
The full options of ImageJ to remove slices are available from the "Delete Slice" click right menu. See the ImageJ User Guide for details.
![]()
"On Line Documentation & Demo Menu":

 On line ressources: documentation, demo images and stacks for training. "About this Toolset" gives an off line short documentation. This last item is also available from the right-click menu.
On line ressources: documentation, demo images and stacks for training. "About this Toolset" gives an off line short documentation. This last item is also available from the right-click menu.

"Version and Update Infos" :
Click on this ImageJ tool bar icon to look for new versions.